limitation on the thickness of specimens for a hardness test|case hardness depth test : exporter exporters exporting During specimen testing or coupon block verification, the spacing between indents, as well as from the material edge, must be properly maintained to prevent any adjacent indents or worked edge from influencing the next test. All of the following are components of an autoclave EXCEPT: valves. temperature gauges. a pressure chamber. pressure gauges. membrane filters.
{plog:ftitle_list}
$159.00
During specimen testing or coupon block verification, the spacing between indents, as well as from the material edge, must be properly maintained to prevent any adjacent indents or worked edge from influencing the next test. Hardness testing does have some limitations and challenges that can affect the accuracy and repeatability of hardness results, some of which are listed below: It is necessary to have properly prepared the surface of the .
During specimen testing or coupon block verification, the spacing between indents, as well as from the material edge, must be properly maintained to prevent any adjacent indents or worked edge from influencing the next test.
Hardness testing does have some limitations and challenges that can affect the accuracy and repeatability of hardness results, some of which are listed below: It is necessary to have properly prepared the surface of the sample to .It is important to note that Brinell hardness testing may not be suitable for materials with very high hardness or thin and small components where a smaller indentation size is desired. In such cases, alternative hardness testing methods like Knoop or Vickers may be more appropriate.The specimen must be thick enough for the indent not to cause any visible deformation on the underside of the specimen (supporting surface). This means that, according to the standard, the specimen must be at least eight times thicker than the indentation depth of the Brinell ball.
What is the limitation on the thickness of specimens for a hardness test? Explain. Calculate the minimum thickness for one specimen for the Rockwell test and one for
In order to prevent the test base (e.g. the test anvil) from affecting the test result in any way, a minimum specimen thickness must be observed with the Brinell method (acc. to ISO 6506). This minimum specimen thickness must be eight times the .
A sample should have a minimal thickness that is at least ten times the indentation depth is expected to be attained. There are minimum thickness recommendations for regular and superficial Rockwell methods. Scales. Sometimes it is .Limitation in applying the method on thin specimens of very hard materials (see Brinell method, minimum specimen thickness). The process is slow (by comparison with the Rockwell method). The test cycle takes somewhere between 30 and 60 seconds, not including the time taken to prepare the specimen.
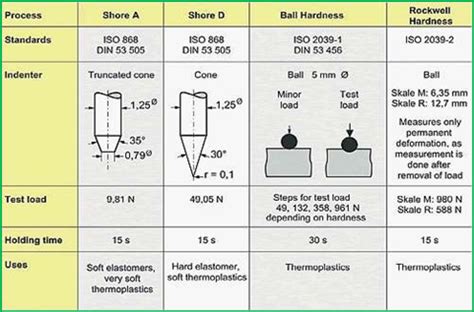
for testing hardness in plastics, like Shore (Durometer), Rockwell, the Ball indentation hardness test and Barcol. This Application Note will focus on hard-ness testing of metals, the mechanical preparation of the specimens and the different parameters influencing the in-dentation hardness testing result.The specimen thickness (the specimen thickness must be at least 1.5 times the indentation diagonals, i.e. the minimum specimen thickness must be between 0.085 and 6.5 mm)During specimen testing or coupon block verification, the spacing between indents, as well as from the material edge, must be properly maintained to prevent any adjacent indents or worked edge from influencing the next test. Hardness testing does have some limitations and challenges that can affect the accuracy and repeatability of hardness results, some of which are listed below: It is necessary to have properly prepared the surface of the sample to .
standards for hardness testing
It is important to note that Brinell hardness testing may not be suitable for materials with very high hardness or thin and small components where a smaller indentation size is desired. In such cases, alternative hardness testing methods like Knoop or Vickers may be more appropriate.
hardness testing scale
The specimen must be thick enough for the indent not to cause any visible deformation on the underside of the specimen (supporting surface). This means that, according to the standard, the specimen must be at least eight times thicker than the indentation depth of the Brinell ball.What is the limitation on the thickness of specimens for a hardness test? Explain. Calculate the minimum thickness for one specimen for the Rockwell test and one forIn order to prevent the test base (e.g. the test anvil) from affecting the test result in any way, a minimum specimen thickness must be observed with the Brinell method (acc. to ISO 6506). This minimum specimen thickness must be eight times the .A sample should have a minimal thickness that is at least ten times the indentation depth is expected to be attained. There are minimum thickness recommendations for regular and superficial Rockwell methods. Scales. Sometimes it is .
Limitation in applying the method on thin specimens of very hard materials (see Brinell method, minimum specimen thickness). The process is slow (by comparison with the Rockwell method). The test cycle takes somewhere between 30 and 60 seconds, not including the time taken to prepare the specimen.
for testing hardness in plastics, like Shore (Durometer), Rockwell, the Ball indentation hardness test and Barcol. This Application Note will focus on hard-ness testing of metals, the mechanical preparation of the specimens and the different parameters influencing the in-dentation hardness testing result.
how to calibrate ade honey refractometer
how to calibrate an antifreeze refractometer
hardness testing process
A medical assistant is loading prepackaged hemostats into an autoclave. Which of the following actions should the assistant take to ensure sterilization? Organize the packages loosely without touching the walls of the autoclave.
limitation on the thickness of specimens for a hardness test|case hardness depth test